Continuous Wave or Pulsed Laser for Cutting Metal
What are the differences between continuous wave laser and pulsed laser for cleaning & welding? Let us make a comparison of pulsed laser and CW laser for metal joints, rust removal, paint stripping, and coating removal.
We all know that the types of laser generators include continuous wave lasers (also known as CW lasers) and pulsed lasers. As the name implies, the continuous wave laser output is continuous in time, and the laser pump source continuously provides energy to generate laser output for a long time, thereby obtaining continuous wave laser light. The output power of CW lasers is generally relatively low, which is suitable for occasions requiring continuous wave laser operation. Pulsed laser means that it only works once at a certain interval. The pulsed laser has a large output power and is suitable for laser marking, cutting, welding, cleaning, and ranging. In fact, in terms of working principle, they all belong to the pulse type, but the output laser pulse frequency of the continuous wave laser is relatively high, which cannot be recognized by the human eye.
STYLECNC will explain the difference between these two types of lasers:
Pulsed Laser VS CW Laser
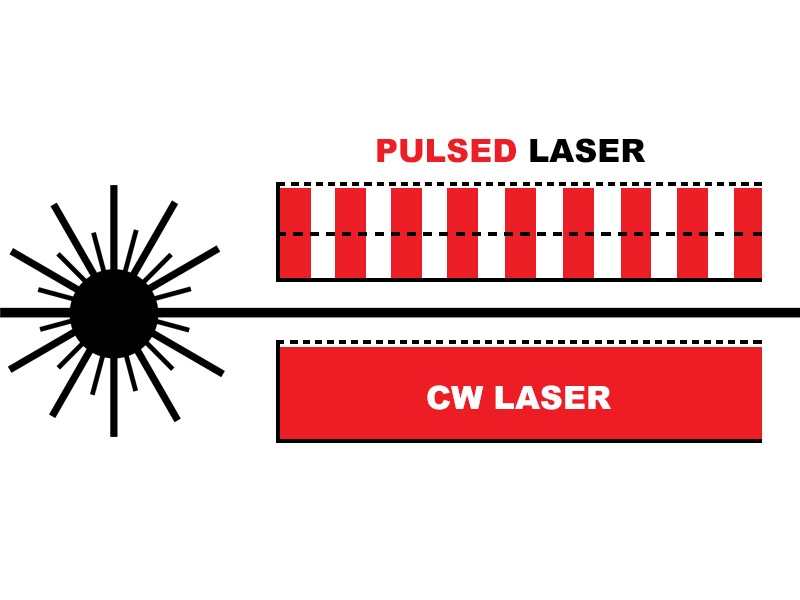
Definition & Principle
1. If a modulator is added to the laser to generate a periodic loss, a part of the output can be selected from so many pulses, which is called a pulsed laser. Simply put, the laser light emitted by the pulsed laser is beam by beam. It is a mechanical form such as a wave (radio wave/light wave, etc.) that is emitted at the same time.
2. In a CW laser, light is generally output once in a round-trip in the cavity. Because the cavity length is generally in the range of millimeters to meters, it can output many times per second, which is called a continuous wave laser. Simply put, the CW laser emits continuously. The laser pump source continuously provides energy to generate laser output for a long time, thereby obtaining continuous wave laser light.
Features
1. Through the excitation of the working substance and the corresponding laser output, the CW laser can continue in a continuous mode for a long period of time. .
2. The pulse laser has a large output power; it is suitable for laser marking, cutting, ranging, etc. The advantage is that the overall temperature rise of the workpiece is small, the heat-affected range is small, and the deformation of the workpiece is small.
Characteristic
1. The continuous wave laser has a stable working state, that is, a steady state. The particle number of each energy level in the CW laser and the radiation field in the cavity have a stable distribution.
2. Pulsed laser refers to a laser whose pulse width of a single laser is less than 0.25 seconds and only works once at a certain interval.
Working Methods
1. The working mode of the pulsed laser refers to the mode in which the output of the laser is discontinuous and only works once at a certain interval.
2. The working mode of continuous wave laser means that the laser output is continuous, and the output is not interrupted after the laser is turned on.
Output Power
1. The pulsed laser has a large output power.
2. The output power of continuous wave lasers is generally relatively low.
Peak Power
1. CW lasers generally can only achieve the size of their own power.
2. The pulsed laser can achieve many times its own power. The shorter the pulse width, the less the thermal effect, and more pulsed lasers are used in fine processing.
Consumables & Maintenance
1. Pulse laser generator: need to be maintained frequently, and consumables will be available later.
2. Continuous wave laser generator: It is almost maintenance-free, and no consumables are required in the later stage.
CW Laser Cleaning VS Pulsed Laser Cleaning
Laser cleaning is an emerging material surface cleaning technology that can replace traditional pickling, sandblasting and high-pressure water gun cleaning. The laser cleaning machine adopts portable cleaning head and fiber laser, which has flexible transmission, good controllability, wide applicable materials, high efficiency and good effect.
The essence of laser cleaning is to use the characteristics of high laser energy density to destroy the pollutants attached to the surface of the substrate without damaging the substrate. According to the analysis of the optical characteristics of the cleaned substrate and the pollutants, the laser cleaning mechanism can be divided into two categories: one is to use the difference in the absorption rate of the pollutants and the substrate to a certain wavelength of laser energy, so that the laser energy can be fully absorbed. The pollutants are absorbed, so that the pollutants are heated to expand or vaporize. The other type is that there is little difference in the laser absorption rate between the substrate and the pollutant. A high-frequency, high-power pulsed laser is used to impact the surface of the object, and the shock wave causes the pollutant to burst and separate from the surface of the substrate.
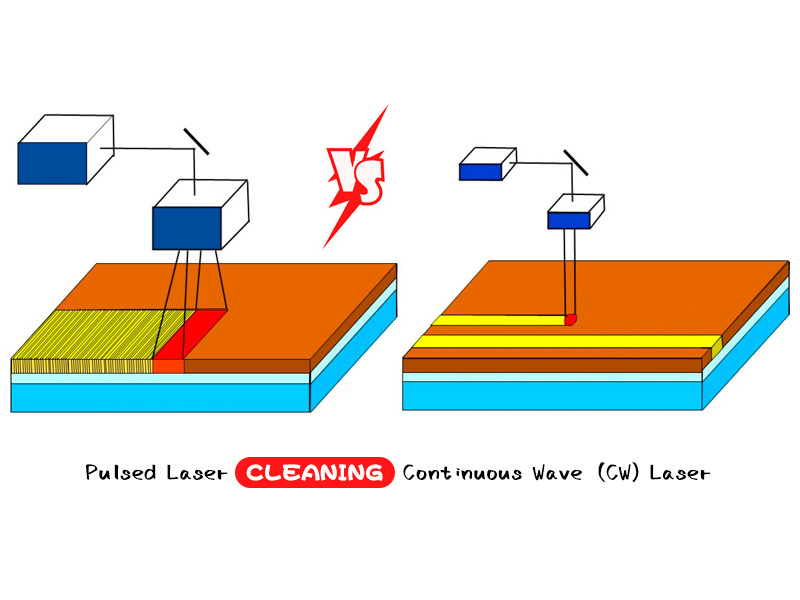
In the field of laser cleaning, fiber laser has become the best choice for laser cleaning light source due to its higher reliability, stability and flexibility. As the two major components of fiber lasers, continuous fiber lasers and pulsed fiber lasers occupy a dominant position in macroscopic material processing and precision material processing, respectively.
The removal of rust, paint, oil and oxide layer on metal surfaces is currently the most widely used field of laser cleaning. Floating rust removal requires the lowest laser power density, and can be achieved by using ultra-high-energy pulsed lasers or even continuous wave lasers with poor beam quality. In addition to the dense oxide layer, it is generally necessary to use a MOPA laser with a near-single-mode pulse energy of about 1.5mJ with a high power density. For other pollutants, an appropriate light source should be selected according to its light absorption characteristics and the ease of cleaning. STYLECNC's series of pulsed and continuous wave laser cleaning machines are suitable for the application of super large energy coarse spot and high energy fine spot respectively.
Under the same power conditions, the cleaning efficiency of pulsed lasers is much higher than that of continuous wave lasers. At the same time, pulsed lasers can better control the heat input and prevent the substrate temperature from being too high or micro-melting.
CW lasers have an advantage in price, and can make up for the gap in efficiency with pulsed lasers by using high-power lasers, but high-power CW lasers have greater heat input and increased damage to the substrate.
Therefore, there are fundamental differences between the two in application scenarios. With high precision, it is necessary to strictly control the heating of the substrate, and the application scenarios that require the substrate to be non-destructive, such as molds, should choose a pulsed laser. For some large steel structures, pipes, etc., due to the large volume and fast heat dissipation, the requirements for damage to the substrate are not high, and continuous wave lasers can be selected.
CW Laser Welding VS Pulsed Laser Welding
Laser welding is to use high-energy laser pulses to locally heat the material in a small area. The energy of the laser radiation diffuses into the interior of the material through heat conduction, and the material is melted to form a specific molten pool. Laser welding is one of the important aspects of the application of laser material processing technology. Laser welding machines are mainly divided into pulse laser welding and continuous wave laser welding.
Laser welding is mainly aimed at the welding of thin-walled materials and precision parts, and can realize spot welding, butt welding, stitch welding, sealing welding, etc., with high aspect ratio, small weld width, small heat affected zone, small deformation, and fast welding speed. The welding seam is flat and beautiful, no need or simple treatment after welding, the welding seam is of high quality, has no pores, can be precisely controlled, the focusing spot is small, the positioning accuracy is high, and it is easy to realize automation.
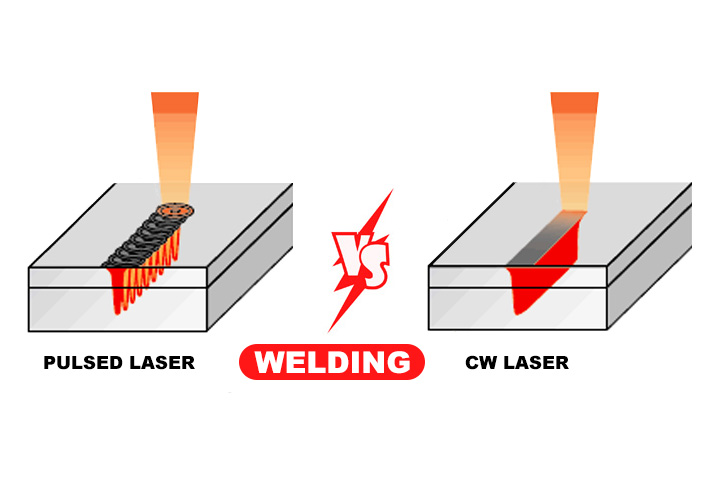
Pulse laser welding is mainly used for spot welding and seam welding of sheet metal materials. Its welding process belongs to the heat conduction type, that is, laser radiation heats the surface of the workpiece, and diffuses into the material through heat conduction to control the waveform, width, peak power and repetition frequency of the laser pulse and other parameters. , to form a good connection between the workpieces. The biggest advantage of pulse laser welding is that the overall temperature rise of the workpiece is small, the heat-affected range is small, and the deformation of the workpiece is small.
Most of continuous wave laser welding are high-power lasers with a power of more than 500 watts. Generally, such lasers should be used for plates above 1mm. Its welding mechanism is deep penetration welding based on pinhole effect, with large aspect ratio, which can reach more than 5:1, fast welding speed and small thermal deformation. It has a wide range of applications in machinery, automobiles, ships and other industries. There are also some low-power CW lasers with powers ranging from tens to hundreds of watts, which are widely used in plastic welding and laser brazing industries.
Continuous wave laser welding is mainly performed by continuously heating the surface of the workpiece with a fiber laser or a semiconductor laser. Its welding mechanism is deep penetration welding based on pinhole effect, with large aspect ratio and fast welding speed.
Pulse laser welding is mainly used for spot welding and seam welding of thin-walled metal materials with a thickness of less than 1mm. The welding process belongs to the heat conduction type, that is, laser radiation heats the surface of the workpiece, and then diffuses into the material through heat conduction. Parameters such as waveform, width, peak power and repetition rate make a good connection between workpieces. It has a large number of applications in 3C product shells, lithium batteries, electronic components, mold repair welding and other industries.
The biggest advantage of pulse laser welding is that the overall temperature rise of the workpiece is small, the heat-affected range is small, and the deformation of the workpiece is small.
Laser welding is a fusion welding, which uses a laser beam as an energy source and impacts on the joint of the weldment. The laser beam can be guided by a flat optical element, such as a mirror, and then projected onto the weld seam by a reflective focusing element or mirror. Laser welding is non-contact welding, no pressure is required during the operation, but inert gas is required to prevent oxidation of the molten pool, and filler metal is occasionally used. Laser welding can be combined with MIG welding to form laser MIG composite welding to achieve large penetration welding, and the heat input is greatly reduced compared to MIG welding.
Source: https://www.stylecnc.com/blog/pulsed-laser-vs-cw-laser.html
0 Response to "Continuous Wave or Pulsed Laser for Cutting Metal"
Post a Comment